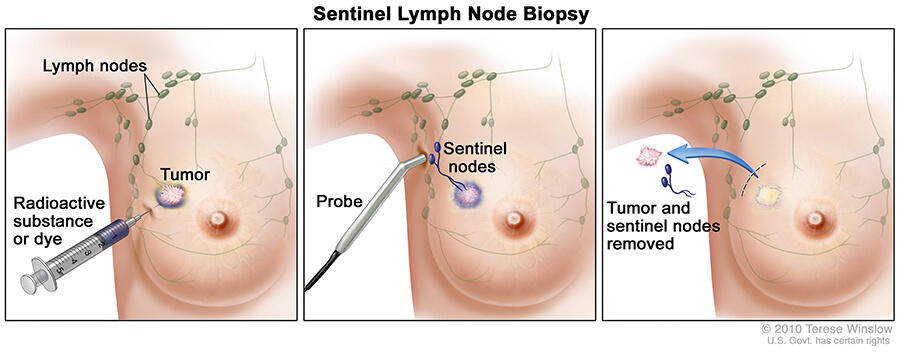
Patients with small early stage breast cancer will most often have a lumpectomy these days. During the same surgery, the surgeon will inject either a radioactive dye or blue dye around the tumor and track the dye to the first 2-3 lymph nodes, called sentinel nodes. In about 30% of patients, a sentinel node will contain previously undetected cancer spread. If the sentinel lymph nodes are normal without cancer, there is a >95% chance the remaining lymph nodes in the area are also normal. If only microscopic disease was found in the sentinel lymph node, there was a 17% chance of further lymph nodes with microscopic amounts of cancer. Because a full axillary lymph node dissection led to more arm swelling (30%) and mobility (20%) issues, a couple more randomized trials were done to show radiation could take care of the microscopic disease without further nodal surgery.
AMAROS and ACOSOG Z0011 enrolled early stage patients that clinically had small breast cancers and no enlarged lymph nodes on physical exam. Sentinel nodes were taken and if positive, half the patients enrolled were randomized to receive just radiation alone vs the other half had a full lymph node surgery with radiation. Even though 33% of patients had additional axillary lymph nodes if a full dissection was performed, there was no difference in cancer cure rates. Arm lymphedema (swelling) was 25% with a full lymph node dissections vs 12% with just the sentinel lymph nodes removed. Thus, the majority of patients will not need a full axillary dissection since radiation can cure microscopic disease left behind.
No lymph node treatment at all?
Most women will now get an ultrasound in addition to mammogram when a suspicion for cancer is found. The ultrasound is able to see enlarged lymph nodes before they are even felt by a physician.
The SOUND trial randomized over 1400 women with early stage breast cancer and no suspicious axillary lymph nodes on ultrasound to either sentinel lymph node sampling with lumpectomy or just lumpectomy alone. In the enrolled favorable population of <2cm primary tumors, only 13% had a positive axillary lymph node with sampling. With adequate adjuvant treatment (>90% responsive to estrogen blockage, 90% receiving whole breast and axillary radiation), there was no difference in cancer cure rate. These results were confirmed by the INSEMA randomized trial including over 5000 women.
Summary
Physical exam by a doctor detects lymph node metastasis in about 70% of early breast cancer patients vs ultrasound detection rate of 87%. In women older than 70 with small estrogen-responsive breast cancers, treatment with lumpectomy alone (without axillary dissection in 60% of patients) followed by estrogen blockade showed only a 3% axillary failure rate. Thus, the Society for Surgical Oncology recommends omitting any axillary treatment in these older women. Radiation after lumpectomy alone for these women can be given to just the partial breast without expecting more than a 3% axillary failure rate, or the whole breast including the axilla to make the axillary recurrence rate near 0%.
